DTM coordinator and Partners have the joint responsibility to cooperate to obtain useful and usable data that support humanitarian response. Using a predictable and commonly agreed process helps field colleagues minimize time and optimize results in cooperation. The Pocket Guide to the shared approach guides colleagues at each step of the process. The Comic Strips is a fun way to learn more on DTM and Partners Cooperation!
Summary of Planning Process
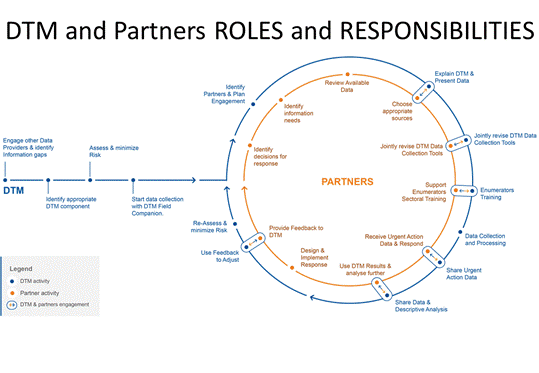
- When setting up a new DTM exercise, DTM team has to provide data in a short timeframe, and therefore time for engagement is limited. DTM can coordinate with other data producers (e.g., in IMWG, Needs Assessment WG…) to understand plans & main information gaps.
- DTM will start data collection using the Data Dictionary questions, with the descriptive analysis for sectoral questions suggested in the Field Companion (developed together by Global DTM Support, Global Clusters, AoRs, and other Global Sectoral Experts).
- DTM may by consulting with OCHA (or the response coordination body, e.g., authorities) and Inter Sectoral fora (e.g., ICCG)
- Once the initial round is complete, partners receive the first data and analysis, they may be able to adapt the questionnaire to meet their information needs.
- DTM explains to Partners methodology, strengths and limitations of the DTM component used in the response (e.g., for the Multi Sectoral Location Assessment they can use Frequently Asked Questions on DTM for Clusters, Presentations in English, French, and Spanish on DTM.
- Partner identifies Information Needs for response. See: Pocket guide to shared approach (page 11 and 12), and Mapping: DTM MSLA Data commonly used by Partners, and examples of sectoral Analytical Frameworks
- Partner identifies how each need link to their use of the information (See Field Companion: Columns “D - Information Need” & “L - Example of Use”)
- Partner approach DTM coordinator with list of information needs that can be obtained through the non-sectoral expert Key Informants and Observation methodology at Community level that DTM MSLA uses. (See: Decision making tree for Clusters WG and Partners on using DTM, as well as Handout Methods and Information, and Data-collection techniques and appropriate use for each technique, form the UNHCR Needs Assessment Handbook.
- Partner and DTM jointly develop appropriate questions (See DTM Field companion (EXCEL) for suggestions), and agree on data sharing modalities (See: Data-sharing Modalities)
- Partner and DTM jointly agree on DTM and Partner roles in analysis (See: Options for Analysis for DTM and Partners).
- Partner and DTM agree on modalities to provide further feedback to DTM in following rounds (See: Providing, Collecting and Acting on Useful feedback)
- Partner and DTM jointly verify with cultural experts that questions are context-appropriate (in the translation used for the exercise) and do no harm to population, enumerators and organizations (See: Do-No Harm Checklist (English, French, Spanish)) to ensure that DTM questions do not put enumerators, organizations or the community at risk
- Partner colleagues are mindful in their requests of the impact of each additional question on the capacity to quickly provide necessary data. DTM Coordinators try to include as many questions as possible, however will exclude questions not in line with the methodology, questions that may be putting enumerators or community members at risk, and questions not clearly linked to their use for response. In addition, DTM may also need to limit the number of questions in the questionnaire.
- Partner colleagues verify that the questions will provide the information the clusters need through a mock-up descriptive analysis (done by DTM or Cluster IMO). (For DTM Field Companion questions most mock-ups are already done, in columns: “ J - Chart” and “K - Narrative”)
- Partner may support DTM with specific sectoral training for enumerator, if needed (e. g., on definitions). (See examples on Trainings for DTM and Partners).
Available Tools
- A detailed description of the steps is in the Pocket Guide to the shared approach in: https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/predictable-approach .
- DTM&Partners Cooperation in Comics (English, Spanish, French), is a Visual illustrates steps of DTM and Partners cooperation; https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-toolkit/dtm-partners-toolkit
- A visual Flow Chart Planning DTM Location Assessment with Data Users illustrates the joint planning actions in details https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/predictable-approach
- A summary on the Planning Process for DTM & Partners Cooperation, in: https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/predictable-approach
- DTM Field Companions include specific information needs that Global experts identified for most sectors: https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/field-companion-sectoral-questions-location-assessmentt. Field companion is available in two formats:
- PDF (one page one question): https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/field-companion-pdf,
- EXCEL (one row one question): https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/field-companion-excel
