-
Countries
-
Data and Analysis
-
Special Focus
-
Crisis Responses
Baseline Assessment

Contact
iomastana@iom.int iomalmaty@iom.int
Language
Russian
Location
Kazakhstan
Period Covered
Feb 15 2024
Apr 30 2024
Activity
- Mobility Tracking
- Baseline Assessment
МTM реализует Оценку базовой мобильности (BMA) в Казахстане для отслеживания мобильности, предоставления информации о численности населения, географическом распределении мждународных трудящихся мигрантов, вернувшихся мигрантов и эмигрантов, причин миграции, а также стран происхождения, возвращения и назначения. Данные собираются на уровне общин (микрорайоны, поселки и деревни) с использованием информации от ключевых информантов и прямых наблюдений.
Оценка базовой мобильности (BMA) была проведена в семи областях Казахстана (Абай, Алматы, Костанай, Кызылорда, Мангистау, Северо-Казахстанская и Туркестанская), а также в трех крупных городах Казахстана: Шымкенте, Алматы и Астане. Это исследование охватило 1,301 сообщество через интервью с 1,923 ключевыми информантами. По оценкам ключевых информантов, в обследованных локациях Казахстана с 2020 года по апрель 2024 года проживало 598,094 международных трудящихся-мигрантов. Одновременно в обследованных локациях находилось 29,853 внутренних мигрантов, а 3,224 казахстанских граждан были зарегистрированы как эмигранты за границей. Кроме того, 17,317 казахстанских мигрантов вернулись из-за границы.

Contact
DTM Somalia, IOMSomaliaDTM@iom.int
Language
English
Location
Somalia
Period Covered
Nov 02 2024
Nov 06 2024
Activity
- Mobility Tracking
- Baseline Assessment
This latest round of Emergency Trends Tracking was initiated in April 2024 to monitor displacements movements during the Gu rainy season. From April to September 2024, DTM teams collected data in up to 22 districts: Afgooye, Afmadow, Baardheere, Baidoa, Balcad, Belet Weyne, Belet Xaawo, Cabudwaaq, Dayniile, Dhuusamarreeb, Doolow, Gaalkacyo, Garoowe, Hodan, Jamaame, Jowhar, Kahda, Kismaayo, Luuq, Waajid, Xudur and Hobyo. As of Round 28, data collection occurred in only 4 districts: Xudur, Waajid, Gaalkacyo and Hobyo districts.
The objective of ETT is to help prioritize humanitarian response and to enable partners to deliver rapid assistance. Based on previous shock induced displacement patterns, the humanitarian community expects that people will continue to move toward urban areas in search of humanitarian services. Consequently, the ETT coverage focuses on the main urban centers and surrounding villages for each assessed district. The data is collected through Key Informant Interviews (KIIs) at the location level, from Sunday to Wednesday every week. It includes information on new arrivals, numbers and demographic of IDPs, reasons for displacement, intentions, humanitarian assistance and priority needs among others.
To facilitate the joint analysis of the CCCM (Camp Coordination and Camp Management) Cluster’s New Arrivals Tracker (NAT) and ETT data, the assistance and needs indicators are identical in both tools.
Contact
DTMUkraine@iom.int
Location
Ukraine
Activity
- Mobility Tracking
- Baseline Assessment
Period Covered
Jul 01 2024 -Aug 31 2024
- Kharkivska (388,410), Dnipropetrovska (377,713), and Kyivska (256,397) Oblasts have the highest numbers of officially registered IDPs.
- Across the country, around 5 per cent of registered IDPs have a state-recognised disability status.
- Sixty per cent of registered IDPs were female, whereas 40 per cent were male. Twenty–nine per cent of registered IDPs were under 18, 48 per cent – between 18 and 59, and 23 per cent were aged 60 and over.
A more detailed version of this dataset at the Hromada level is available. To get access, kindly click on the 'Request Access' button.
Population Groups
IDPs
Survey Methodology
Unit of Analysis Or Observation
Admin Area 2
Admin Area 3
Type of Survey or Assessment
Key Informant
Keywords
Geographical Scope Partial Coverage
Administrative boundaries with available data
The current dataset covers the following administrative boundaries
Contact
DTMUkraine@iom.int
Location
Ukraine
Activity
- Mobility Tracking
- Baseline Assessment
Period Covered
Sep 01 2024 -Oct 31 2024
- Kharkivska (390,872), Dnipropetrovska (379,133), and Kyivska (257,606) Oblasts have the highest numbers of officially registered IDPs.
- Across the country, around 10 per cent of registered IDPs have a state-recognised disability status.
- Sixty per cent of registered IDPs were female, whereas 40 per cent were male. Twenty–five per cent of registered IDPs were under 18, 52 per cent – between 18 and 59, and 23 per cent were aged 60 and over.
A more detailed version of this dataset at the Hromada level is available. To get access, kindly click on the 'Request Access' button.
Population Groups
IDPs
Survey Methodology
Unit of Analysis Or Observation
Admin Area 2
Admin Area 3
Type of Survey or Assessment
Key Informant
Keywords
Geographical Scope Partial Coverage
Administrative boundaries with available data
The current dataset covers the following administrative boundaries
Contact
dtmlebanon@iom.int
Language
English
Location
Lebanon
Period Covered
Oct 10 2023
Nov 10 2024
Activity
- Mobility Tracking
- Baseline Assessment
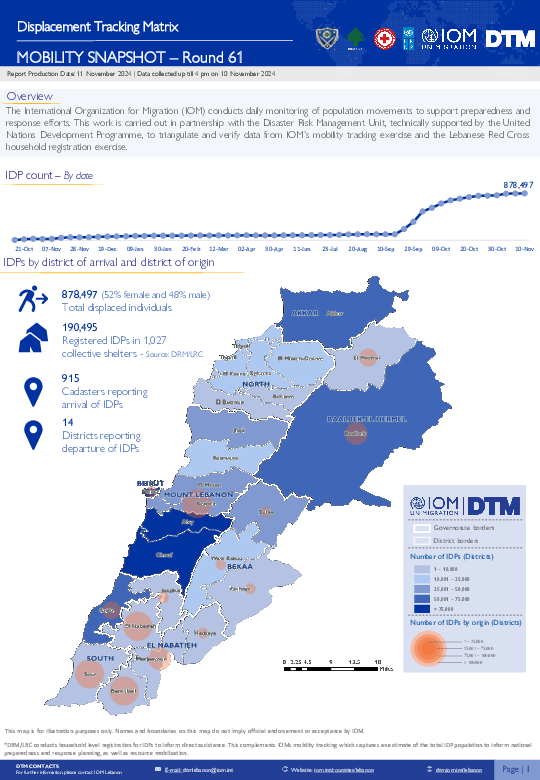
Since October 8 there has been an increase in cross-border incidents between Israel and Lebanon, resulting in the displacement of people both within the South and elsewhere within the country. Since October 10, the Displacement Tracking Matrix (DTM) has been conducting the daily monitoring of population movements. The objective of the exercise is to inform preparedness and response planning.
Contact
dtmlebanon@iom.int
Location
Lebanon
Activity
- Mobility Tracking
- Baseline Assessment
Period Covered
Oct 10 2023 -Nov 06 2024
Since October 8 there has been an increase in cross-border incidents between Israel and Lebanon, resulting in the displacement of people both within the South and elsewhere within the country. Since October 10, the Displacement Tracking Matrix (DTM) has been conducting the daily monitoring of population movements. The objective of the exercise is to inform preparedness and response planning.
To get access kindly click on the 'Request Access' button. Please use your official work email, and specify the organisation name. Thank you.
Population Groups
IDPs
Survey Methodology
Unit of Analysis Or Observation
Admin Area 2
Admin Area 3
Household
Individual
Type of Survey or Assessment
Key Informant
Keywords
Geographical Scope Full Coverage
Administrative boundaries with available data
The current dataset covers the following administrative boundaries

Contact
dtmlebanon@iom.int
Language
English
Location
Lebanon
Period Covered
Oct 10 2023
Nov 06 2024
Activity
- Mobility Tracking
- Baseline Assessment
Since October 8 there has been an increase in cross-border incidents between Israel and Lebanon, resulting in the displacement of people both within the South and elsewhere within the country. Since October 10, the Displacement Tracking Matrix (DTM) has been conducting the daily monitoring of population movements. The objective of the exercise is to inform preparedness and response planning.
Contact
dtmlebanon@iom.int
Location
Lebanon
Activity
- Mobility Tracking
- Baseline Assessment
Period Covered
Oct 10 2023 -Nov 03 2024
Since October 8 there has been an increase in cross-border incidents between Israel and Lebanon, resulting in the displacement of people both within the South and elsewhere within the country. Since October 10, the Displacement Tracking Matrix (DTM) has been conducting the daily monitoring of population movements. The objective of the exercise is to inform preparedness and response planning.
To get access kindly click on the 'Request Access' button. Please use your official work email, and specify the organisation name. Thank you.
Population Groups
IDPs
Survey Methodology
Unit of Analysis Or Observation
Admin Area 2
Admin Area 3
Type of Survey or Assessment
Key Informant
Keywords
Geographical Scope Full Coverage
Administrative boundaries with available data
The current dataset covers the following administrative boundaries

Contact
DTM Somalia, IOMSomaliaDTM@iom.int
Language
English
Location
Somalia
Period Covered
Oct 26 2024
Oct 30 2024
Activity
- Mobility Tracking
- Baseline Assessment
This latest round of Emergency Trends Tracking was initiated in April 2024 to monitor displacements movements during the Gu rainy season. From April to September 2024, DTM teams collected data in up to 22 districts: Afgooye, Afmadow, Baardheere, Baidoa, Balcad, Belet Weyne, Belet Xaawo, Cabudwaaq, Dayniile, Dhuusamarreeb, Doolow, Gaalkacyo, Garoowe, Hodan, Jamaame, Jowhar, Kahda, Kismaayo, Luuq, Waajid, Xudur and Hobyo. As of Round 28, data collection occurred in only 4 districts: Xudur, Waajid, Gaalkacyo and Hobyo districts.
The objective of ETT is to help prioritize humanitarian response and to enable partners to deliver rapid assistance. Based on previous shock induced displacement patterns, the humanitarian community expects that people will continue to move toward urban areas in search of humanitarian services. Consequently, the ETT coverage focuses on the main urban centers and surrounding villages for each assessed district. The data is collected through Key Informant Interviews (KIIs) at the location level, from Sunday to Wednesday every week. It includes information on new arrivals, numbers and demographic of IDPs, reasons for displacement, intentions, humanitarian assistance and priority needs among others.
To facilitate the joint analysis of the CCCM (Camp Coordination and Camp Management) Cluster’s New Arrivals Tracker (NAT) and ETT data, the assistance and needs indicators are identical in both tools.

Contact
DTM Papua New Guinea, iompngmdac@iom.int
Language
English
Location
Papua New Guinea
Period Covered
Oct 22 2024
Oct 25 2024
Activity
- Mobility Tracking
- Baseline Assessment
The Aiya Local Level Government (LLG) in Papua New Guinea’s Southern Highlands province is characterized by its mountainous terrain. The region's geography features creeks that form streams, with the most arable land located along riverbanks. Most of the local population engage in agriculture, relying on this land for sustenance and cash crops.
On the night of October 11, 2024, a severe weather event occurred, marked by heavy rainfall, thunder, and strong winds from 8:30 PM until midnight on October 12. This intense downpour led to landslips and flooding across the six Council Wards of Aiya Rural LLG in the Kagua Erave District, Southern Highlands province. Between October 22 - 25, 2024, the International Organization for Migration (IOM) and the Kagua Erave Community Development Office conducted a Displacement Tracking Matrix (DTM) Rapid Assessment in Aiya Rural LLG to assess damage and guide response efforts.
The flooding and landslips have severely impacted local livelihoods, causing significant damage to homes, food gardens, and water sources. Residents noted they have never encountered flooding and landslips of this magnitude, marking it as unprecedented for the community. The most affected council wards are Kandopa Ward 2, Lakira Ward 1 and Apopa Ward 25. These affected wards are all situated between mountainous regions, making them particularly vulnerable to landslips and flooding.
Pagination
- Previous page
- Page 2
- Next page
