-
Countries
-
Data and Analysis
-
Special Focus
-
Crisis Responses
Iraq – Protection Risks and Concerns Among Travellers Crossing for Work (December 2021 - May 2022)
Contact
IraqDTM@iom.int
Language
English
Location
Iraq
Period Covered
Dec 01 2021
May 30 2022
Activity
- Survey
- Flow Monitoring
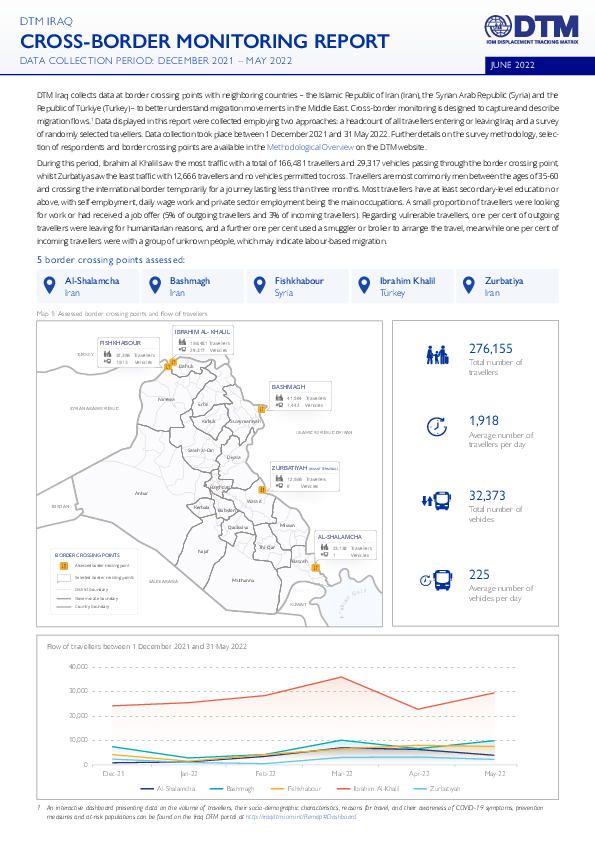
DTM Iraq collects data at border crossing points with neighboring countries – the Islamic Republic of Iran (Iran), the Syrian Arab Republic (Syria) and the Republic of Türkiye (Turkey) – to better understand migration movements in the Middle East. Cross-border monitoring is designed to capture and describe migration flows. Data displayed in this report were collected employing two approaches: a headcount of all travellers entering or leaving Iraq and a survey of randomly selected travellers. Data collection took place between 1 December 2021 and 31 May 2022. Further details on the survey methodology, selection of respondents and border crossing points are available in the Methodological Overview on the DTM website.
During this period, Ibrahim al Khalil saw the most traffic with a total of 166,481 travellers and 29,317 vehicles passing through the border crossing point, whilst Zurbatiya saw the least traffic with 12,666 travellers and no vehicles permitted to cross. Travellers are most commonly men between the ages of 35-60 and crossing the international border temporarily for a journey lasting less than three months. Most travellers have at least secondary-level education or above, with self-employment, daily wage work and private sector employment being the main occupations. A small proportion of travellers were looking for work or had received a job offer (5% of outgoing travellers and 3% of incoming travellers). Regarding vulnerable travellers, one per cent of outgoing travellers were leaving for humanitarian reasons, and a further one per cent used a smuggler or broker to arrange the travel, meanwhile one per cent of incoming travellers were with a group of unknown people, which may indicate labour-based migration.
