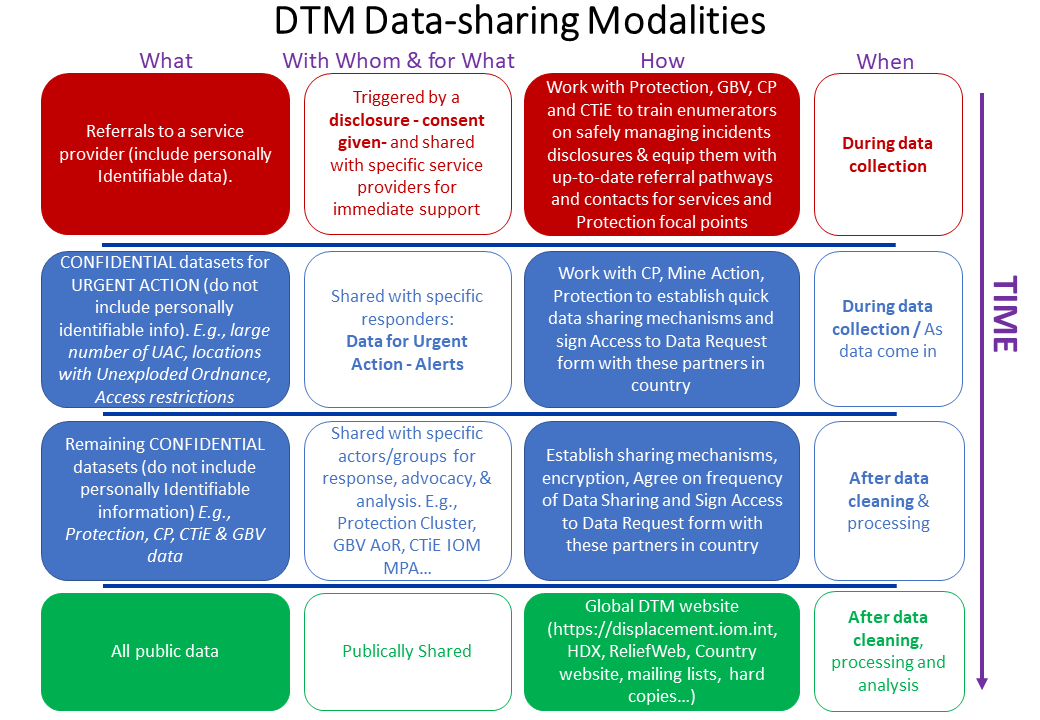
Sharing modality depends on Type of Data
DTM distinguishes three types of data and shares them in three different ways, depending on the sensitivity and potential urgency of use of the data:
- Data for Urgent Action
- Sensitive Data
- Public Data
DTM & Partners should jointly fill Column B, “Dissemination Category” of the DTM Data Analysis Plan (template), before data is collected. (See the suggested template in: DTM&Partners Toolkit:Analysis).
This is to identify the appropriate modality for dissemination of each dataset, ensure swift sharing of data for urgent action and avoid public sharing of sensitive datasets
1. Data for Urgent Action
Data for Urgent actions are those data that partners need right away for their urgent intervention. They vary from context to context. Partners will be able to identify what data they need for urgent action already in the planning phase. Example of Data for Urgent Actions may be:
- Larger than expected number of Unaccompanied Children
- Sudden movement of large population
- Health Alerts
- Explosive Ordnance
Partners should let DTM know in the planning phase what information they need for urgent action, so that DTM is able to identify what information should be shared to which partners for urgent action, and through which means. DTM cannot be expected to know what data partners need for their urgent action.
DTM & Partners will set up the procedure for information sharing BEFORE data collection starts. That includes Data Sharing Agreement (if the data are sensitive), channels for appropriate data sharing, contact focal point and other practical modalities.
Data Sharing Agreements will be developed early, in the planning phase, so that data can be shared quickly and safely once collected.
2. Sensitive Data
Sensitive datasets will only be shared bilaterally with actors who can use them for response, e.g., Protection Actors, Protection Cluster and AoRs. Sharing is defined by Data Sharing Agreements between IOM DTM and Partner at country level.
A guideline was developed to facilitate inter-organizational data sharing while minimizing the risk of doing harm, by ensuring that:
- Sensitive data/information that should not be shared publicly have been identified and documented.
- A data-sharing process for safely sharing sensitive data from DTM to a third party has been discussed and agreed.
3. Public Data
DTM public data and reports are online and available at: https://dtm.iom.int/ (through a search by Country).
In some cases, reports and datasets may be only shared by email to a controlled list. Partners can always contact the DTM coordinator in your country (ask DTMSupport@iom.int for his/her contact details).
Guiding appropriate analysis when sharing data
In order to correctly analyse and use DTM results, Partners need to fully understand the methodology, the questions used and the metadata (information about the dataset that helps understanding the dataset).
DTM and global partners developed a checklist of What to include in DTM reports and datasets to help appropriate analysis of DTM data by partners.
Available Tools
- For examples of Data Sharing forms and guidelines, see: https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/data-sharing
- What to include in DTM reports and datasets to help appropriate analysis of DTM data by partners: https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/reporting
- DTM Clusters Data-sharing Modalities, in: https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/data-sharing
- Guideline for DTM Coordinators Identifying Sensitive Data and Inter-Organizational Data Sharing Pathways, in: https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/data-sharing-guidelines
- DTM Data Sharing Forms: https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/dtm-data-sharing-forms
- Practical ways for safer data by TDH and CartONG, in: https://dtm.iom.int/dtm-partners-toolkit/data-sharing
